Moles and warts
Regular breast examinations are important because they help to detect and treat possible diseases in time, enabling our patients to stay healthy and prevent disease.
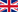
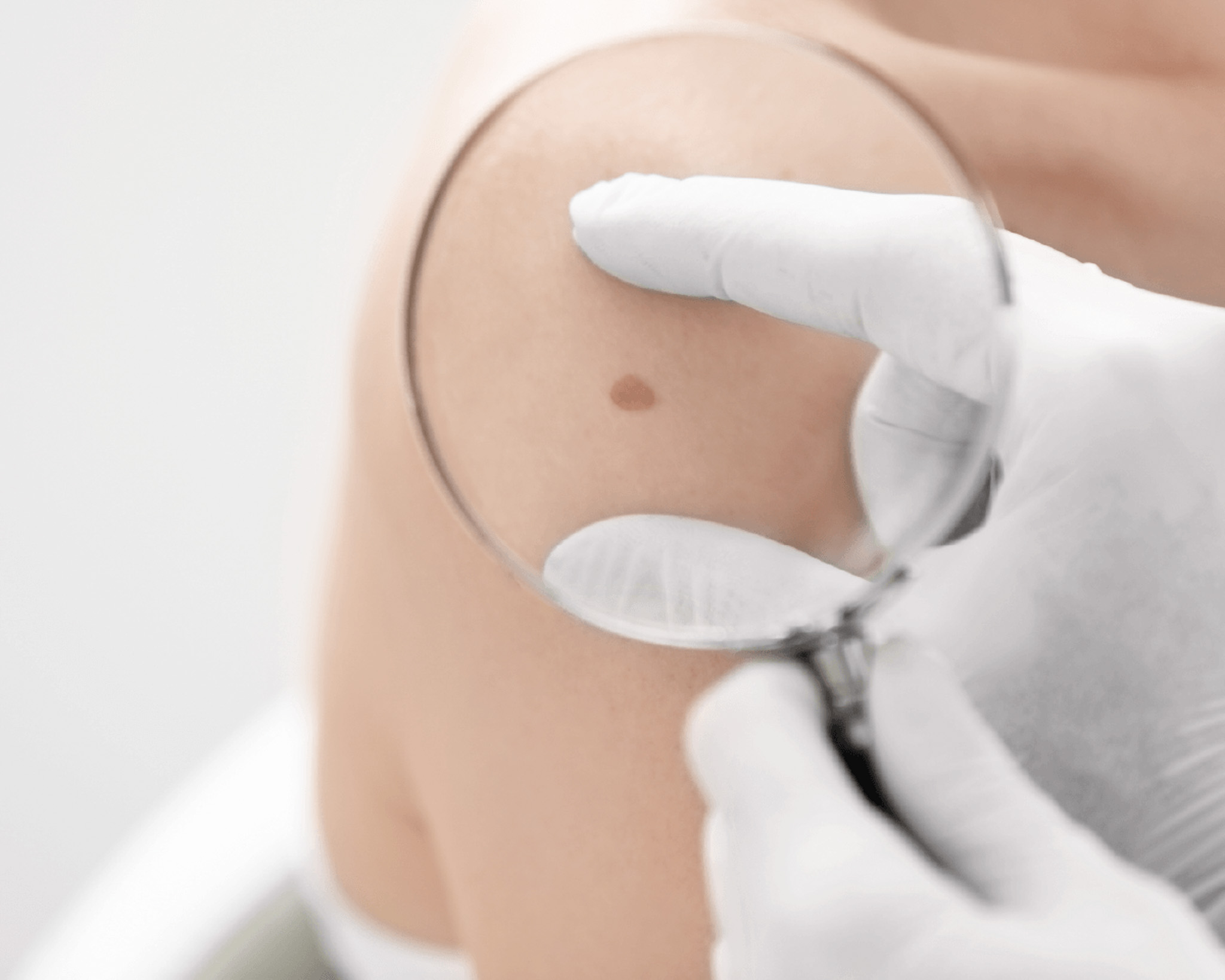
Skin examination, dermatoscopy
The Dermdoc digital dermatoscopy system allows dermatologists to look beyond the surface layers of the skin and detect lesions invisible to the human eye. Digital skin scanning greatly facilitates diagnosis for the dermatologist and increases the chances of early detection of malignant melanoma.
Digital mole screening is a non-invasive method of testing. It is painless and the patient can watch the test on the screen. If detected early, melanoma can be successfully treated and surgically removed. The earlier the melanoma is detected, the better the chances of treatment and the fewer surgical procedures are needed to remove it.
Melanoma develops around existing moles, warts or on apparently normal skin. Pigmented skin rashes or age spots in the form of warts, moles or age spots can occur on any part of the body on any person. Everyone is therefore at risk of developing a malignant lesion, or malignant melanoma, on these areas of skin.
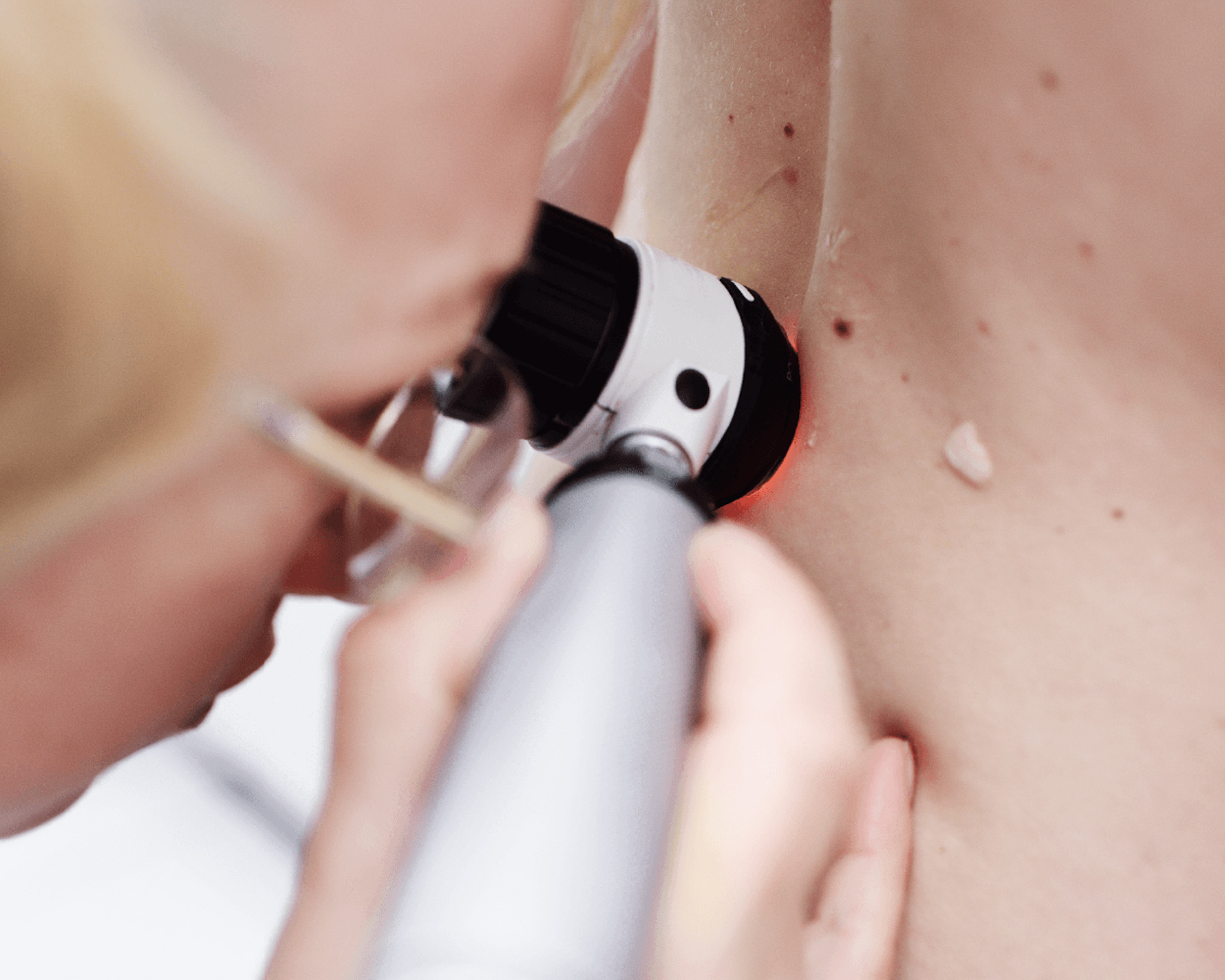
The benefits of digital dermatoscopy:
The patient can watch the examination of the mole on the screen.
Direct diagnosis by microscopy - no biopsy required.
Direct visual examination without the need for a microscope
Unbiased and accurate follow-up of high-risk moles
Clear differentiation between benign and malignant moles, pigmented lesions
Mandatory light and long-term examination of moles, pigmented lesions
Removal of moles and warts
Skin lesions protruding from different skin surfaces: moles, warts, etc. are removed by laser after dermoscopic examination. However, most pigmented skin lesions can only be removed surgically after consultation with a dermatologist. After examination and recommendation by a dermatologist, the lesion is excised under local anaesthesia in the form of a laurel leaf in the intact tissue and sent for histological examination. The wound is closed with stitches. The surgical wound is minimally painful and can be closed with oral analgesics. The wound must be kept clean and dry, and the dressing should be changed every 2 days after washing with an antiseptic solution. Stitches should be removed 10-14 days after surgery. The surgical wound will heal with a linear scar that will fade and become less dense over time.
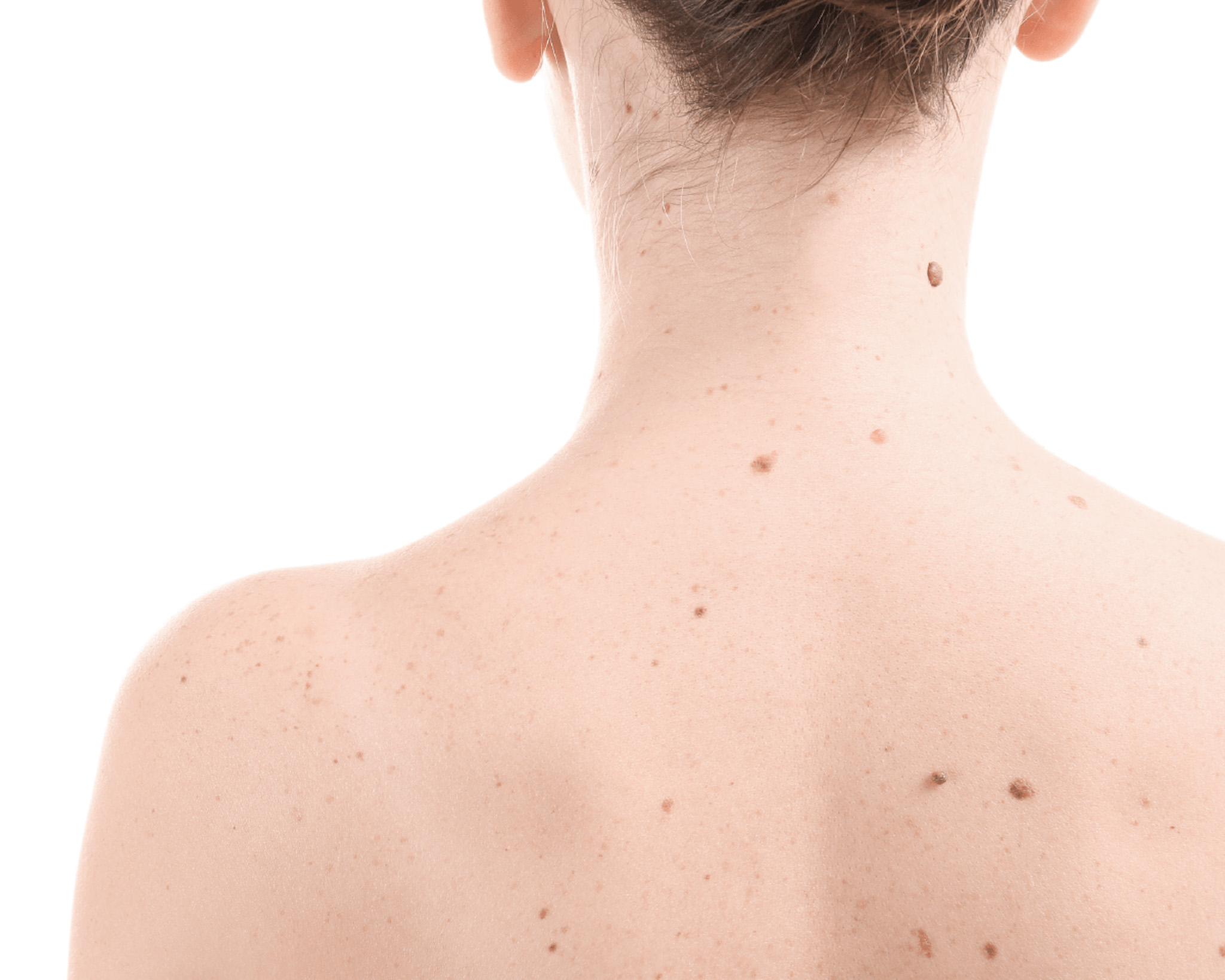
Lesions under the skin
The most common are lipoma and atheroma. A lipoma is a benign, so-called fatty tumour, surrounded by a capsule of subcutaneous fatty tissue that is separated from the surrounding area. In neglected cases it can grow to a significant size.
Atheromas (trichylemma cysts) originate from blocked sebaceous glands, occur most commonly on the hairy scalp and back, can grow, become inflamed and sometimes discharge foul-smelling sebum from the lesion. It is advisable to remove the atheroma as soon as possible, surgically excising it with a capsule. Do not wait for the inflammatory phase (this causes considerable pain, swelling and is more difficult to remove surgically). Surgical excision is performed under local anaesthesia, with histopathological examination of the mass removed. The skin is sutured during surgical removal. The sutures are removed after 2 weeks.
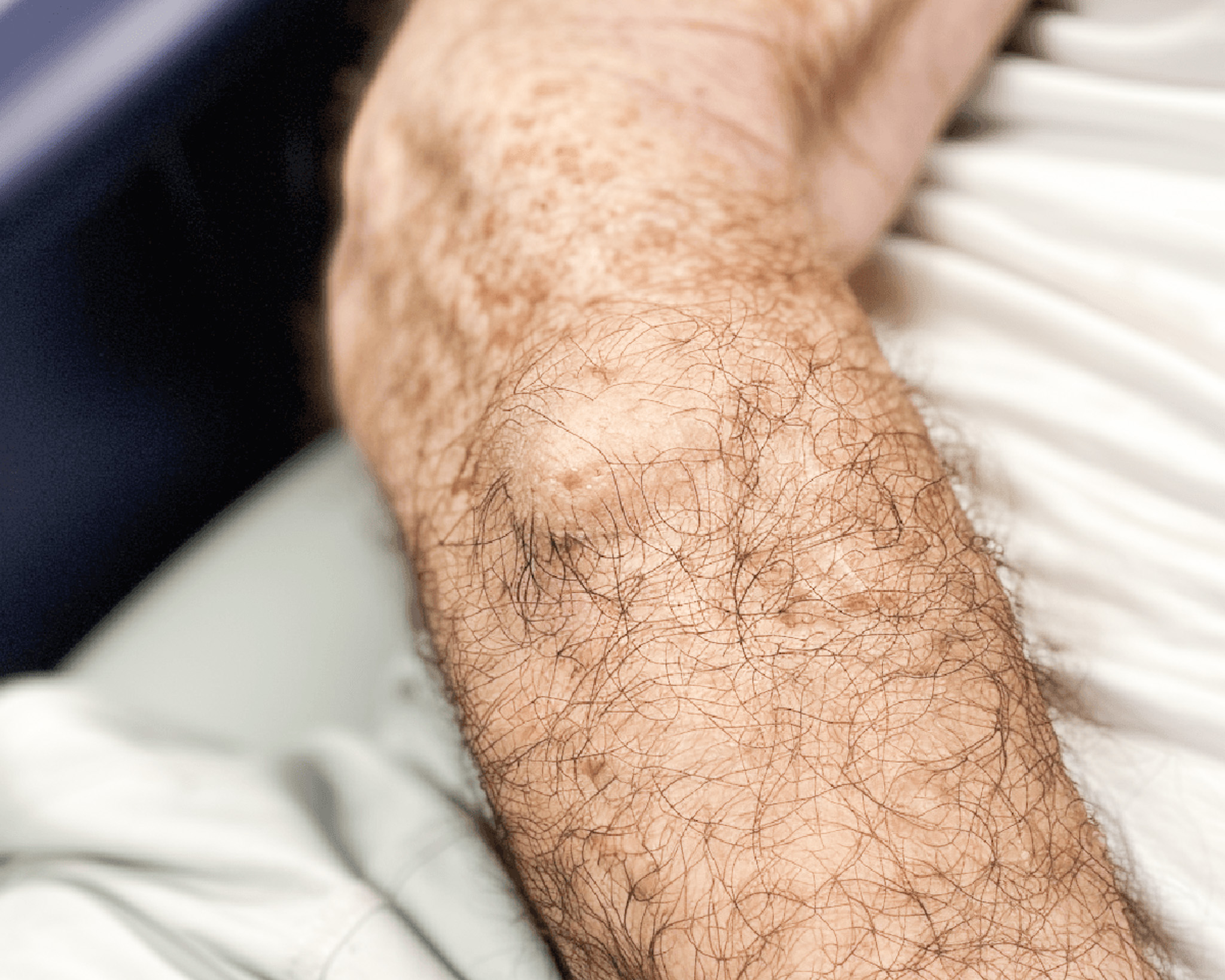
Common warts (papilloma)
Warts are growths on the skin and mucous membranes (mouth or genitals) that can be caused by more than 100 types of human papillomavirus (HPV). Common warts are skin coloured, rough to the touch and spherical in shape. HPV causes thickening of the top layer of skin. Common warts are found on damaged areas of the body, such as the elbows, knees and backs of the hands.
Warts are usually spread through contact between people. The virus is not highly contagious, but can cause infection through damaged skin. HPV can spread in a similar way in a person's own body.
Common warts are painless, with one exception: if the wart develops on the sole of the foot.
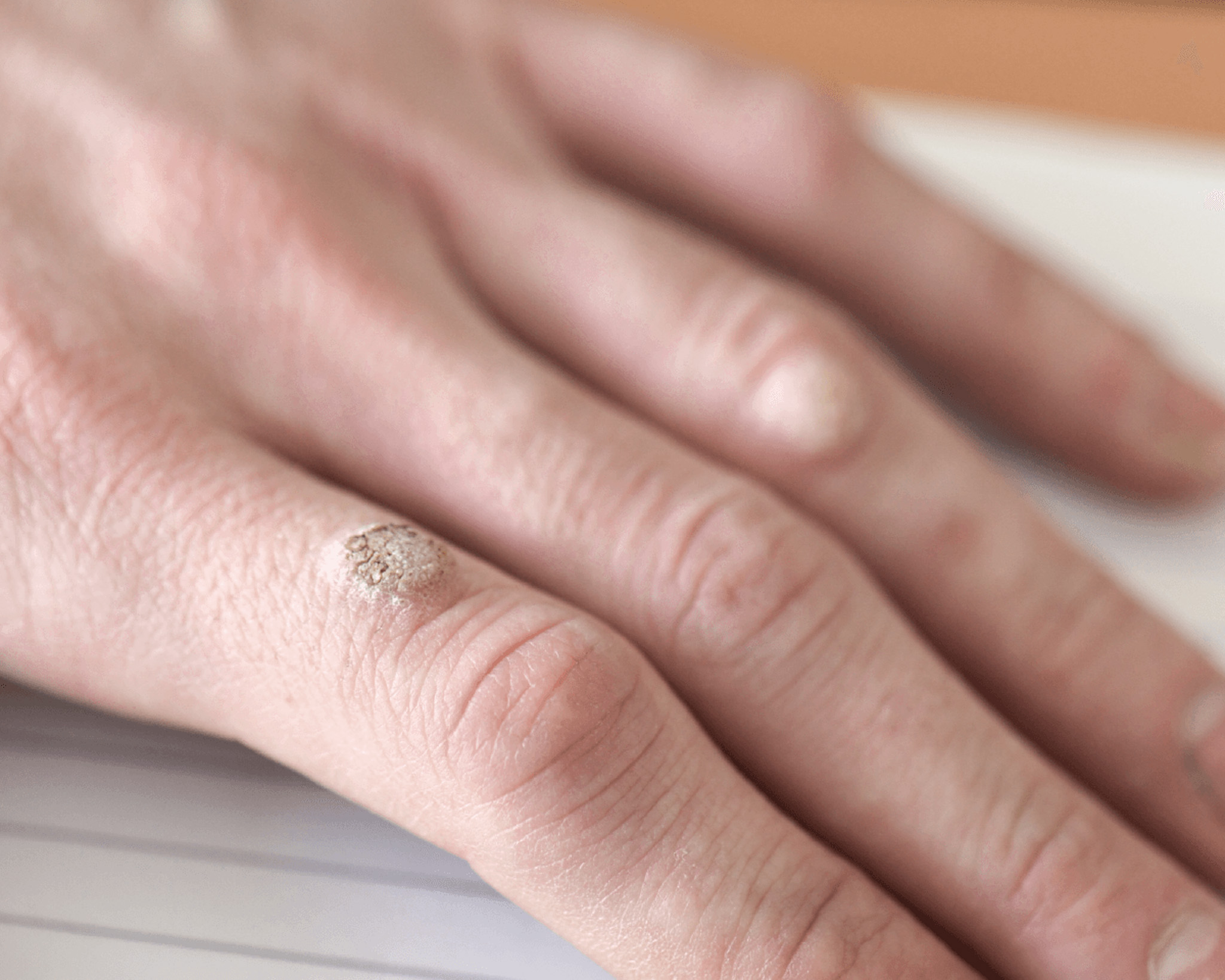
Common viral wart (verruca vulgaris)
They most commonly occur on the hands and feet. They cause cosmetic and functional complaints (difficulty in gripping and walking, pressure pain). They are removed by conventional surgery or laser surgery.

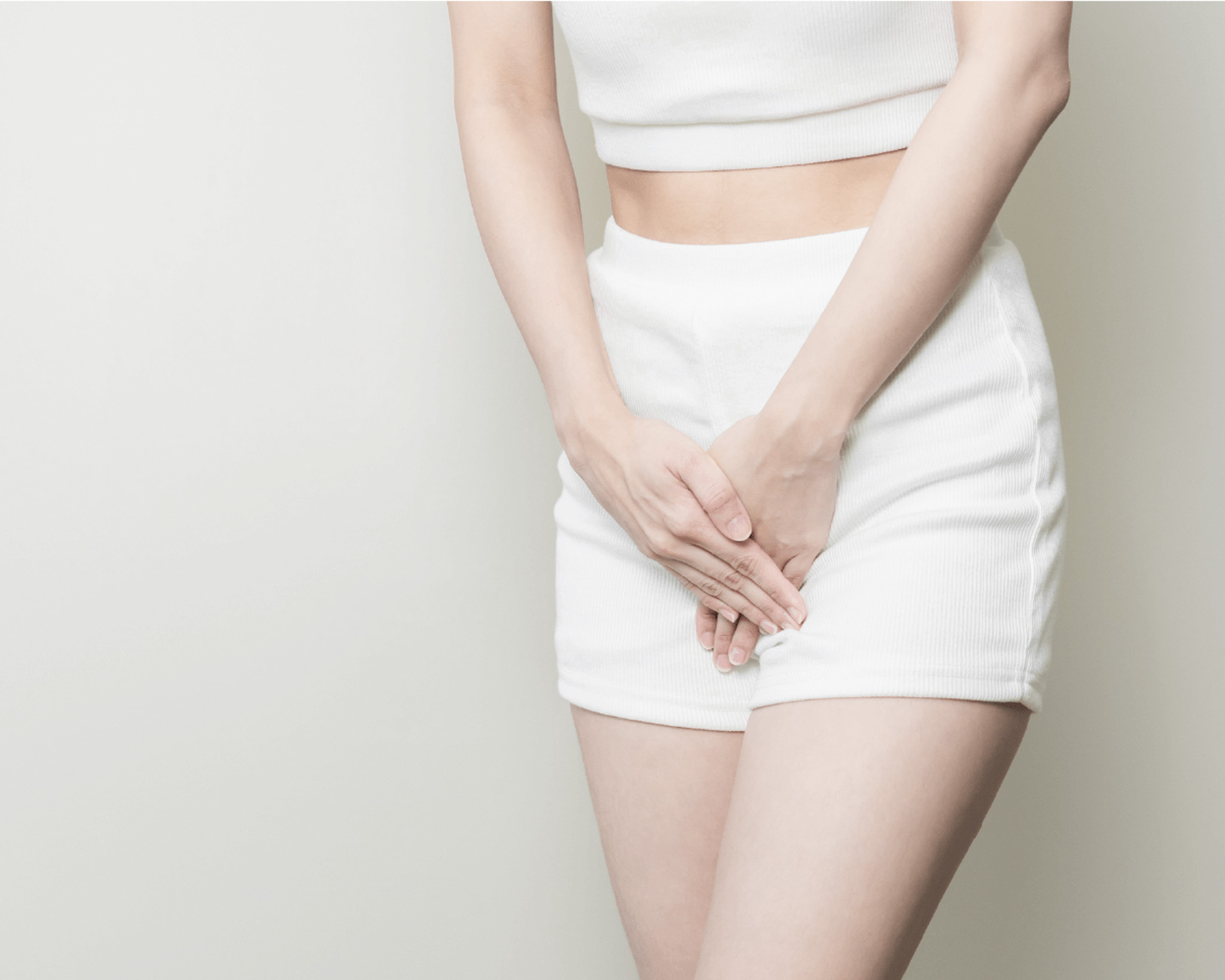
Genital warts (condyloma)
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the world. HPV is directly linked to the cause of genital warts (formerly known as genital warts).
HPV has also been known to cause cervical cancer in women, and more recently it has been discovered to play a role in various cancers of the anus, vulva, vagina, penis and throat. Genital warts (medically known as condylomata acuminata) are the most easily recognised signs of genital HPV infection. However, it is important to note that there are more people with HPV infection who do not have visible genital warts. Genital warts are typically non-painful, soft, flesh-coloured growths that appear in the genital area (penis, vagina, anus). Genital warts can also be found inside the vagina, on the uterus, in the anus. Genital warts can be prominent or flat, large or small, cauliflower-like in appearance, occurring in clusters.
Genital warts can be easily detected by a doctor by eye examination. Although warts are not a health risk, many people choose to have them removed by their doctor for various reasons. The most common reason is that large growths can be irritated by rubbing caused by clothing.ű
No or minimal scarring is expected after laser treatment of papilloma and condynoma, depending on the size of the warts.

PRICE LIST
Laser removal and examination of moles, fibroids, warts
From 2 pieces 3500 Ft/piece (for diameters less than 1cm)
*The fee for a dermatological consultation is not charged in case of a simultaneous instrumental procedure!
**Region: more favourable calculation in cases where several skin lesions need to be laser removed within the same region.
For condyloma: the patient can be declared cured after 2 negative controls. In these cases, a control examination fee of 20 000 HUF (every 3 weeks, at least twice) or a surgical fee if a new removal is necessary.
Surgical removal of moles, lipomas, atheromas
Mole, atheroma, lipoma | Surgical removal | Histology (Skin excisio, excision size matters) | Stitch removal |
|---|---|---|---|
1 piece | 39 000 Ft on trunk (up to 2cm diameter) head: 49 000 Ft | 13 000 Ft | Free |
2 pieces | 65 000 Ft on trunk head: 79 000 Ft | 26 000 Ft | Free |
3 pieces | 79 000 Ft on trunk (up to 2cm diameter) head: 100 000 Ft | 39 000 Ft | Free |
Csatlakozzon hozzánk és legyen a Medaid csapat tagja!
Aktuális szabad pozíció: orvosi adminisztrátor
A jelentkezéseket az info@medaid.hu e-mail címre várjuk!